
News
Dr. Jiao Yang: A detailed explanation of the progress of research on metal bipolar plates and their coatings
"Preparing highly conductive and corrosion-resistant coatings, which are the most basic requirements for metal plate plating. Also finding the right hardness can improve the stability of the whole electric stack; the thinner the coating is made, the lower the body resistance; and low-cost and batch preparation can advance the commercialization of metal plates." Dr. Yang Jiao of the Central Research Institute of Vision Group said at the 2022 (4th) GaoGong Hydrogen Power Industry Summit (South China Station) event.

The following is a selection of presentations:
The market for metal sheets is expanding rapidly as the demand for high-powered metal stacks increases. From a technical point of view, metal plates have significant advantages in terms of bending resistance, compressive strength, electrical conductivity and mass production, but they also have some disadvantages to overcome, most typically poor corrosion performance, and there is still a need to find more suitable plating solutions to improve corrosion resistance.
Functional characteristics of fuel cell bipolar plates
The function of the bipolar plate is to provide a gas flow path to prevent the hydrogen in the cell chamber from colluding with the oxygen and to establish a current path between the cathode and anode in series. The bipolar plate is one of the important components of a fuel cell, accounting for approximately 80% of the weight and 24% of the cost of a PEMFC stack.
The fuel cell bipolar plate is the "skeleton" of the stack and is assembled with the membrane electrodes to form the stack. It plays an important role in the fuel cell as a single cell link, transporting fuel, current collection and conduction, supporting the stack and MEA, removing the heat generated by the reaction and draining the water produced by the reaction.
The thickness of the bipolar plate should be as thin as possible to reduce the resistance to current and heat conduction, while maintaining a certain mechanical strength and good resistance effect.
Classification of fuel cell bipolar plates
The three types of bipolar plate materials currently available on the market for hydrogen fuel cells are graphite, metal and composite materials. Compared to graphite and composite plates, which are generally used in medium and low power reactors, metal plates are increasingly reused in high power reactors due to their superior forming properties in the ultra-thin state.
Specifically, the preparation of metal plates includes pole plate configuration design, precision mould design and processing, precision forming of ultra-thin plates, long-life composite nano-coating and integrated sealing technology, among which the choice of base material and plating layer of metal plates is worthy of attention.
Research progress of metal bipolar plate plating
Research progress of metal bipolar plate plating metal bipolar plate surface plating materials are mainly: conductive polymer composites, precious metal surface modification materials, nitrogen-doped or carbon-based alloy materials. General metal bipolar plate substrates include: stainless steel, titanium, nickel and aluminium. Comparing these substrates in terms of chemical stability, cost, processability, mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity, it can be seen that stainless steel substrates have excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, as well as high mechanical properties. The manufacturing and processing costs are also relatively low, which is one reason why most manufacturers choose stainless steel substrates.
However, stainless steel substrates also have some drawbacks to overcome, such as poor corrosion resistance in acidic conditions, ionic precipitation that impairs PEM properties and surface oxide films that can lead to high contact resistance (ICR).
Corrosion resistance is a very important property of sheet metal. How does corrosion arise? Mainly from stress corrosion, as well as chemical and electrochemical corrosion. Stress corrosion is the stress concentration caused during the stamping production process, resulting in dislocations, vacancies, grain boundaries, etc.; chemical and electrochemical corrosion mainly has crevice corrosion and pitting corrosion, the main places where it occurs are particles, adhesions, inclusions and intermetallic compounds on the surface. So the need for plating to improve the performance of the whole substrate.
There are metal plating, carbon film plating, nitride film and carbide film. Among them, carbon film coating: alternating substrate bias deposition method: coating deposited in 15 alternating cycles at 0.6 V potential, coating thickness of 242 nm, corrosion current density of 0.297 μA/cm², ICR value of 3.58 mΩ-cm²; multi-layer carbon-based coating modified bipolar plate, can effectively reduce coating defects and improve the corrosion resistance of the plate
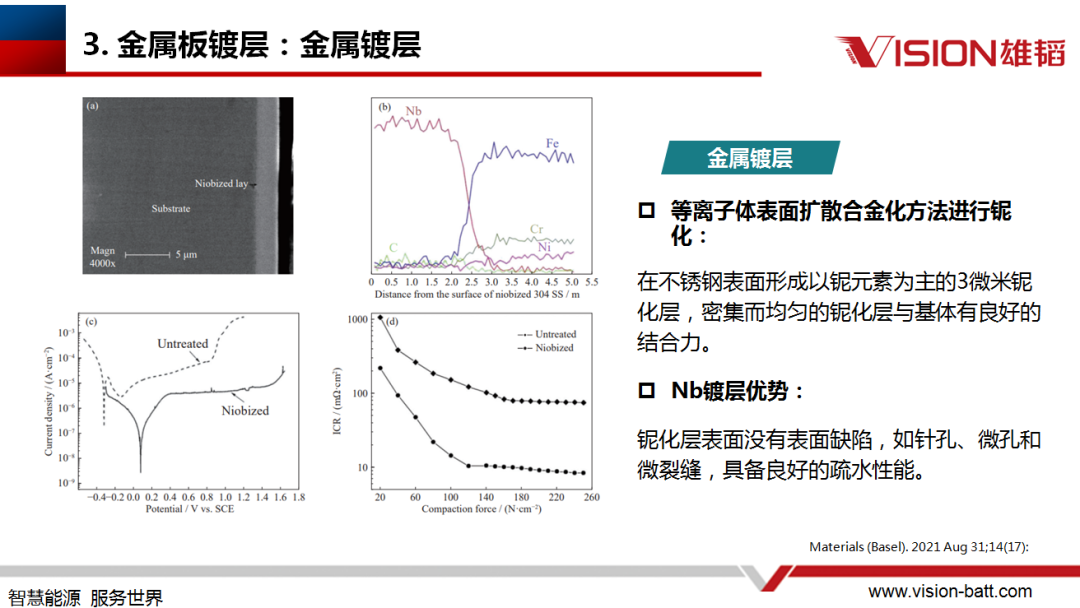
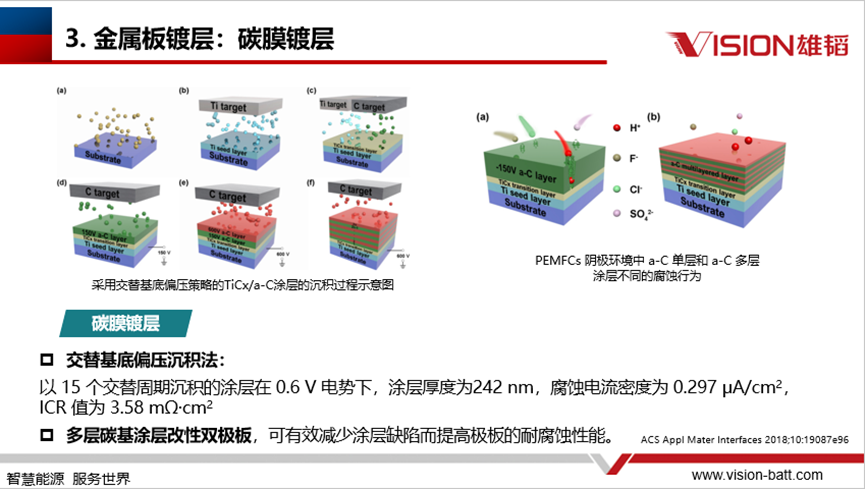
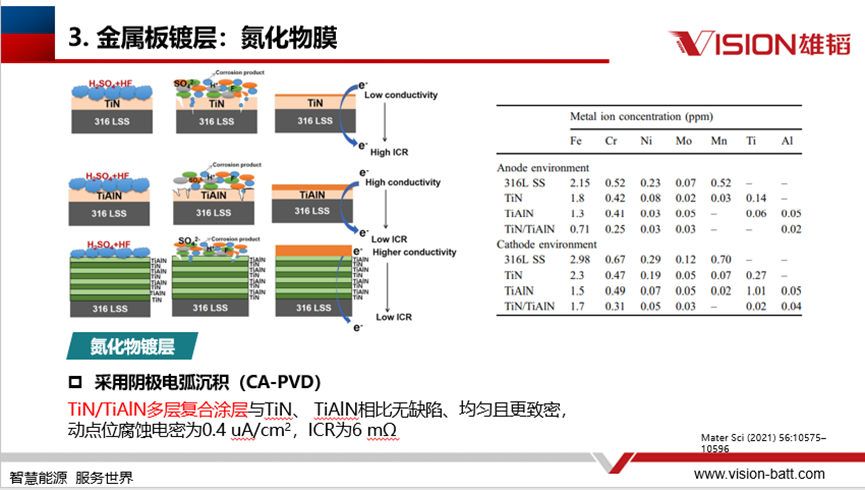
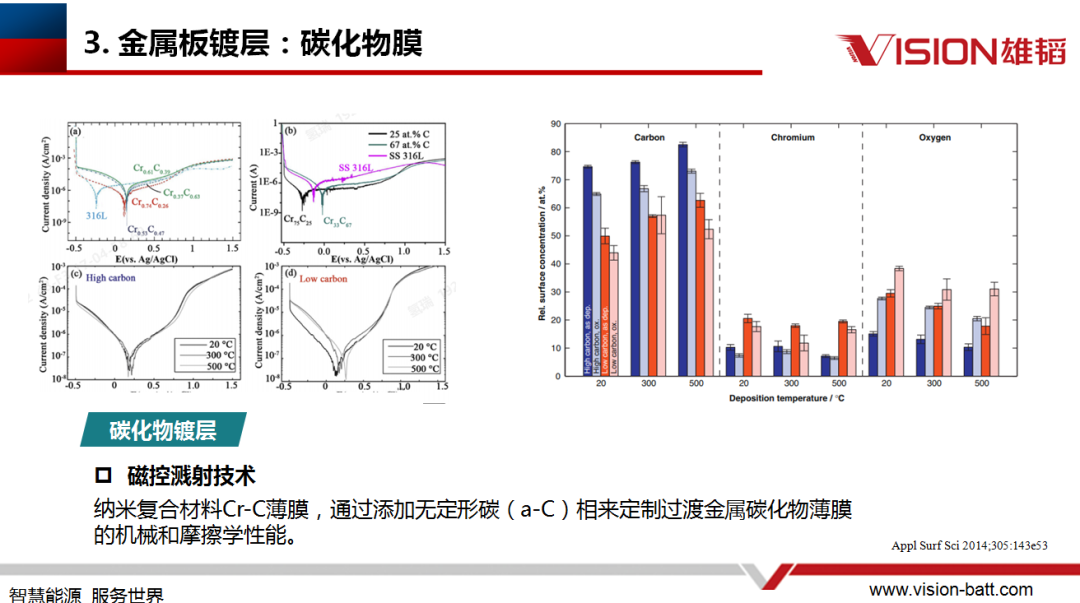
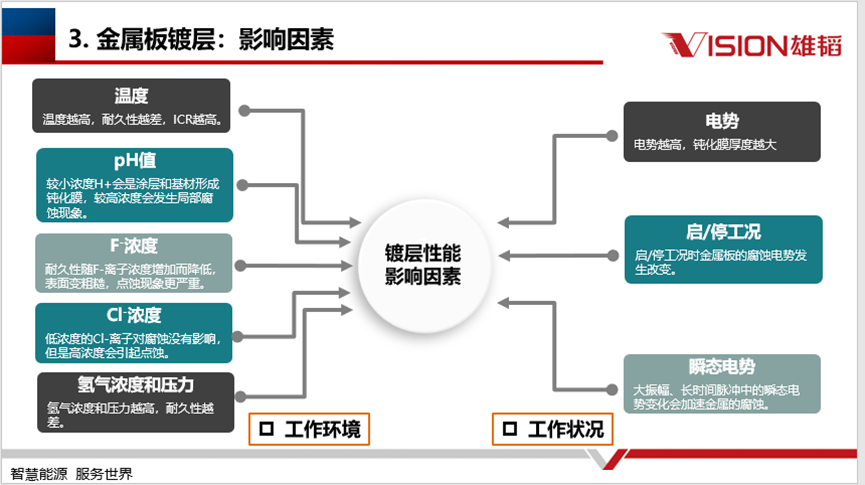
The factors affecting the plating can be divided into two main categories: working environment and working conditions. During the operation of the stack, changes in temperature, pH value, hydrogen concentration and pressure will affect its performance; including potential, start/stop conditions, transient potential, etc. will also have an impact on it. Therefore, it is necessary to optimise the plating structure in order to improve the overall performance of the reactor.
At the end of the presentation, Dr. Yang Jiao pointed out that the preparation of highly conductive and corrosion-resistant coatings is the most basic requirement for metal plate plating. In addition, finding the right hardness can improve the stability of the whole stack; the thinner the coating, the lower the resistance; and the lower cost and batch preparation can advance the commercialization of metal plates.


